PAM-STAMP
The heat analysis of alloy sheet hot stamping forming process and experiments indicate that the transition process from Austenite to Martensite by controlling the sheet heating and cooling temperature is the foundation of heat forming. Only when the cooling rate reaches or surpasses the critical cooling rate, Austenite can be transformed to Martensite directly. Critical cooling rate of sheet is related to the elements of critical water flow rate, die cooling system design, cooling medium, dented die medium and the like. Under the condition, that the elements of die structure, cooling system, cooling medium and the like are defined, critical cooling rate is a constant value. As a result, through controlling critical water flow rate, hot forming transition process and hot forming requirements can be guaranteed to overcome the excessive rebound, cracking, forming force increase, easy die wear and the like in hot forming process.
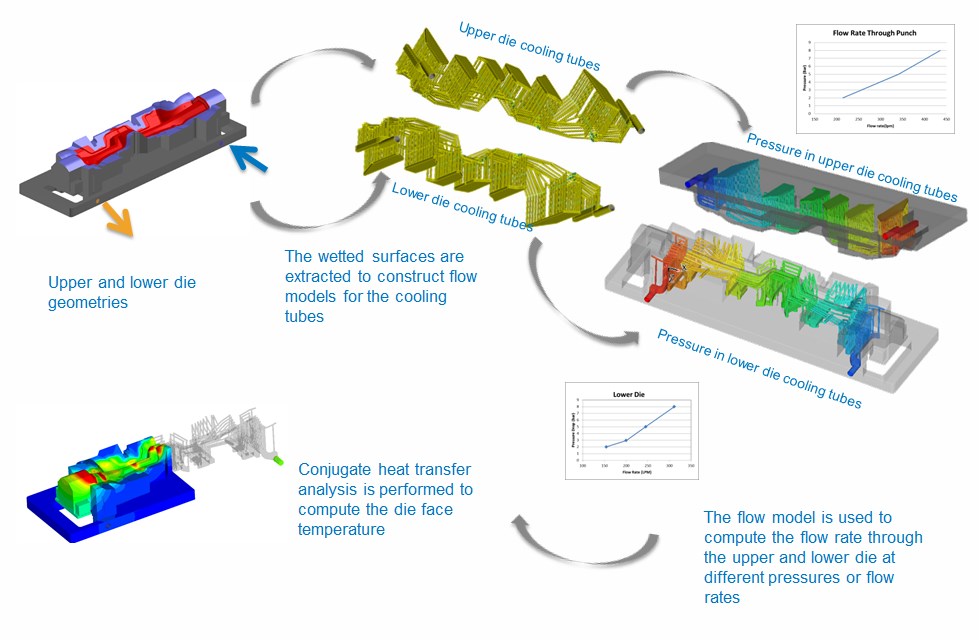
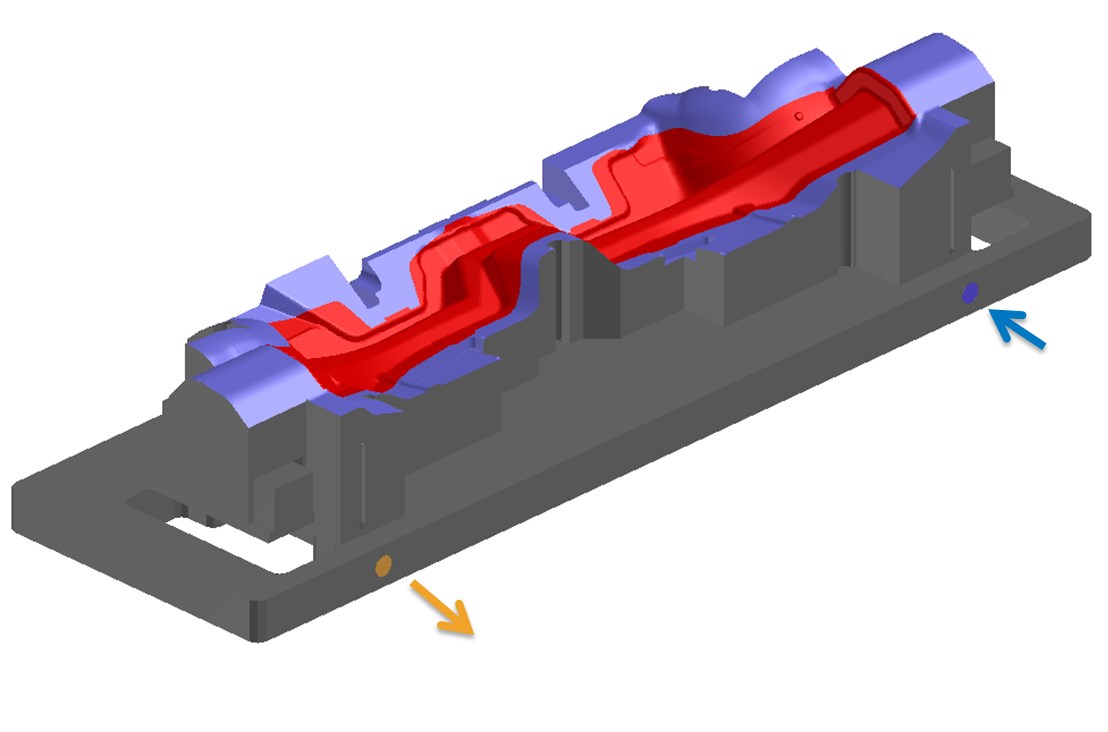
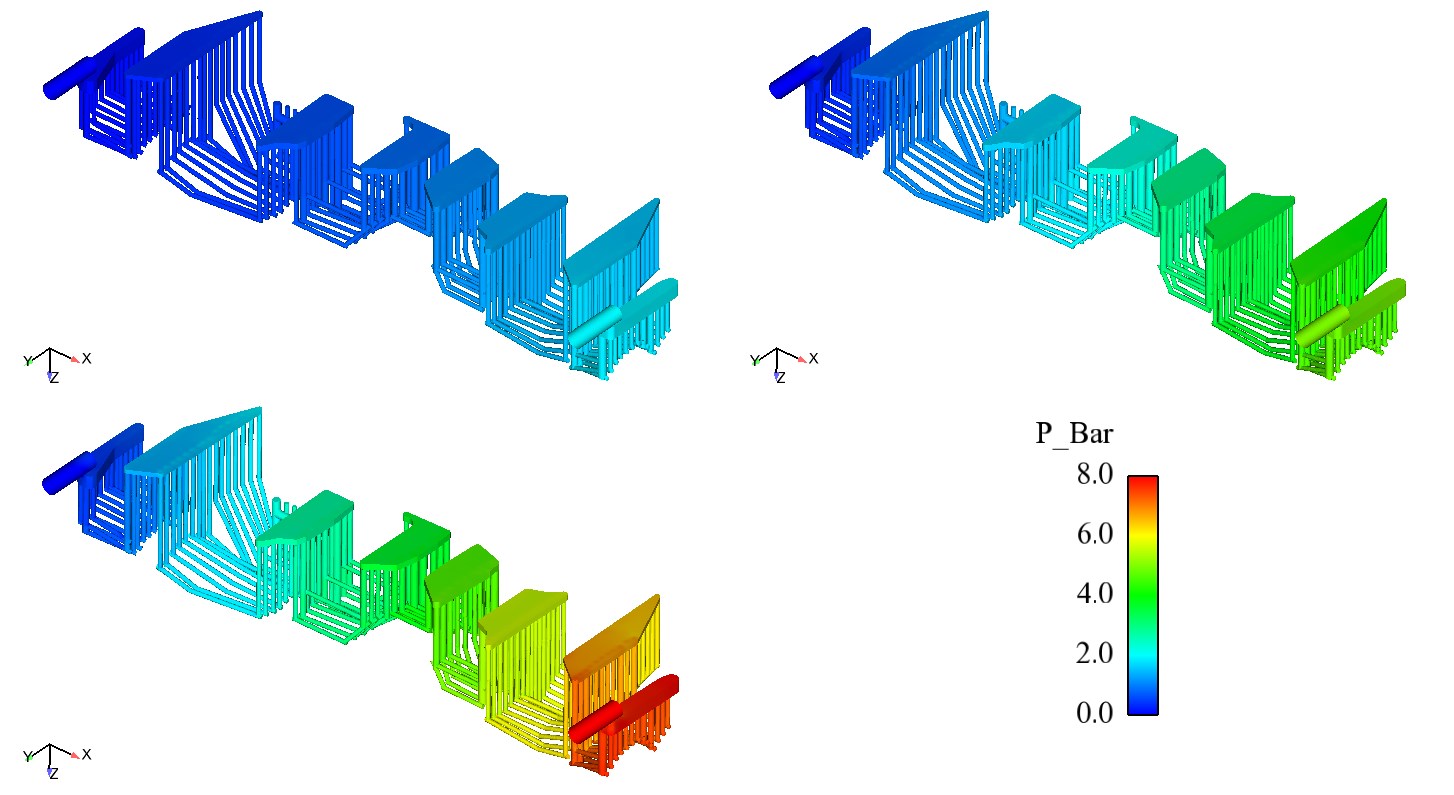
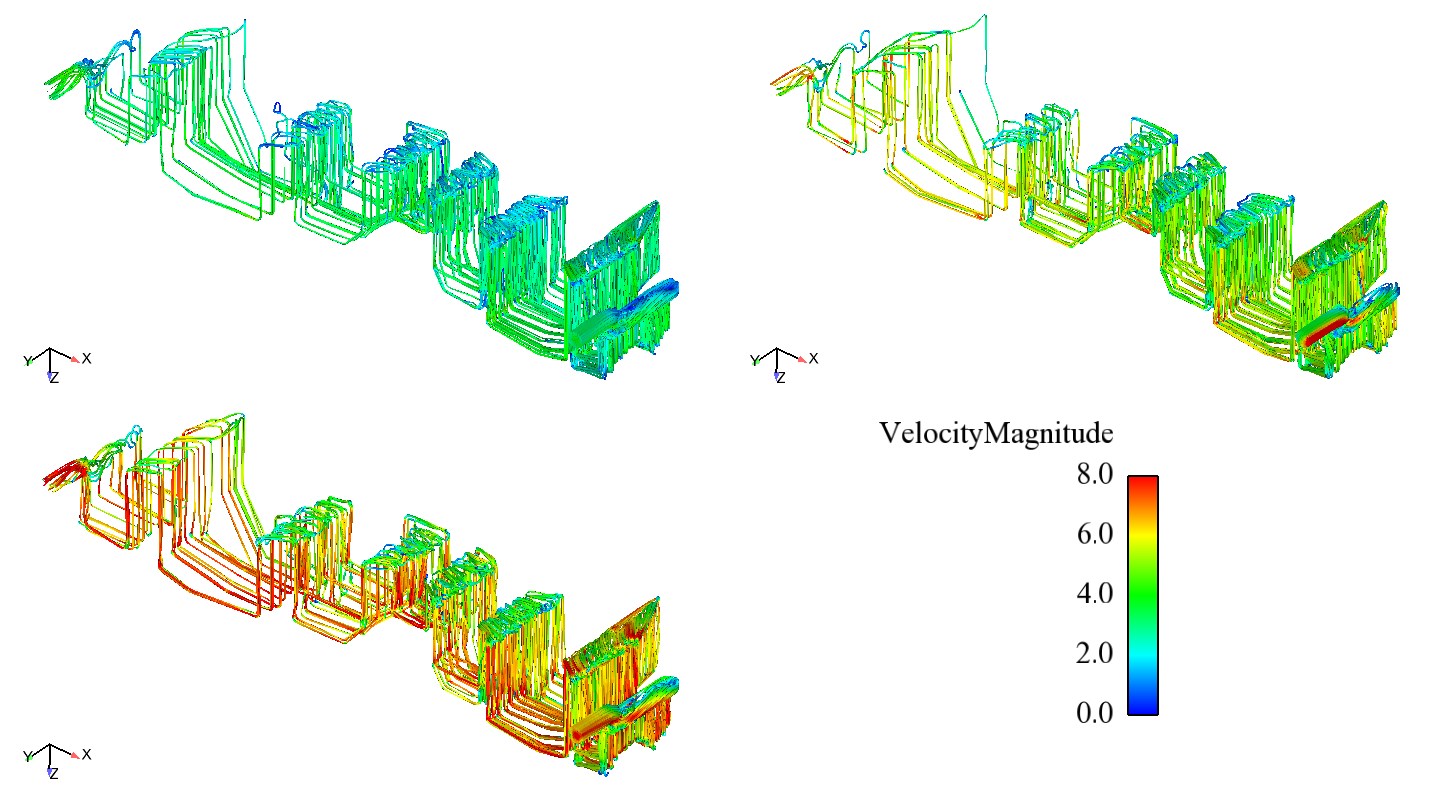
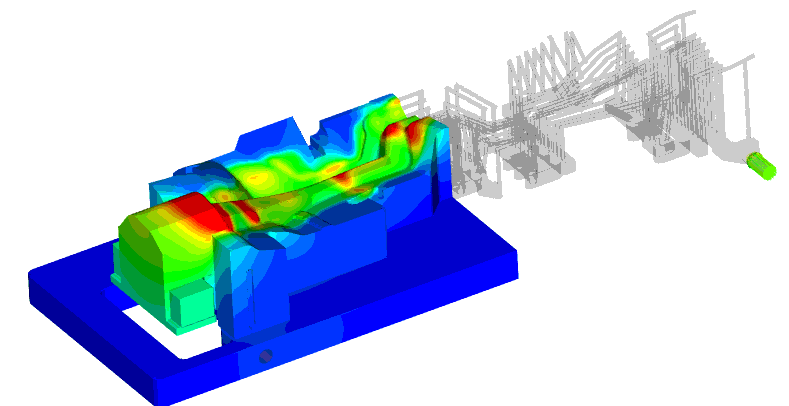
ACE+ CFD solver is used to compute the coolant flow rate through the upper and lower die cooling tubes. Fig. 21 shows the pressure distribution in the upper die cooling tube at 2, 5, and 8 bars. The CFD analysis also predicts the heat transfer coefficient in the cooling tubes. The heat transfer coefficients, which are computed by ACE+, are mapped to PAM STAMP to compute the tool face temperature.